How To Download Eclipse For Windows 10
Eclipse for Java
How To Install Eclipse and Get Started with Java Programming
(on Windows, macOS and Ubuntu)
Eclipse (@ world wide web.eclipse.org) is an open-source Integrated Evolution Environment (IDE) supported by IBM. Eclipse is pop for Java application development (Coffee SE and Java EE) and Android apps. Information technology as well supports C/C++, PHP, Python, Perl, and other web project developments via extensible plug-ins. Eclipse is cantankerous-platform and runs under Windows, Linux and macOS.
Eclipse Versions
The various versions are:
- Eclipse 1.0 (Nov vii, 2001): based on an earlier Coffee IDE chosen VisualAge from IBM.
- Eclipse 2.0 (June 28, 2002)
- Eclipse 2.i (March 28, 2003)
- Eclipse 3.0 (June 25, 2004)
- Eclipse three.1 (June 28, 2005)
- Eclipse iii.ii (June 30, 2006) (Callisto - named after ane of the Jupiter's Galilean moons): started annual simultaneous release of all the related Eclipse projects.
- Eclipse 3.3 (June 25, 2007) (Europa - named subsequently another Jupiter'south Galilean moons)
- Eclipse 3.iv (June 19, 2008) (Ganymede - named after yet some other Jupiter's Galilean moons)
- Eclipse iii.v (June 12, 2009) (Galileo - named after the dandy 17th century scientist and astronomer Galileo Galilei)
- Eclipse 3.6 (June 23, 2010) (Helios - named after god of the sun in Greek Mythology)
- Eclipse iii.7 (June 23, 2011) (Indigo)
- Eclipse 4.ii (June 27, 2012) (Juno)
- Eclipse 4.3 (June 2013) (Kepler)
- Eclipse four.4 (June 2014) (Luna)
- Eclipse 4.5 (June 2015) (Mars)
- Eclipse iv.6 (June 2016) (Neon)
- Eclipse 4.7 (June 2017) (Oxygen)
- Eclipse four.8 (June 2018) (Photon)
- Eclipse 2018-09 (four.9) (starting quarterly release), Eclipse 2018-12 (iv.10)
- Eclipse 2019-03 (4.eleven), Eclipse 2019-06 (four.12), Eclipse 2019-09 (4.13), Eclipse 2019-12 (4.fourteen)
- Eclipse 2020-03 (4.xv), Eclipse 2020-06 (4.16), Eclipse 2020-09 (4.17), Eclipse 2020-12 (4.xviii)
- Eclipse 2021-03 (4.nineteen), Eclipse 2021-06 (four.20), Eclipse 2010-09 (4.21), Eclipse 2021-12 (4.22)
- Eclipse 2022-03 (four.23)
How to Install Eclipse IDE 2021-12 for Java Developers
How to Install Eclipse on Windows
Step 0: Install JDK
To apply Eclipse for Java programming, you demand to first install Coffee Development Kit (JDK). Read "How to Install JDK for Windows".
Step i: Download
Download Eclipse from https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/packages/. Choose "Eclipse IDE for Java Developers" and "Windows x86_64" (e.g., "eclipse-java-2021-12-R-win32-x86_64.zip" - about 313MB) ⇒ Download.
Footstep 2: Unzip
To install Eclipse, but unzip the downloaded file into a directory of your selection (e.g., "c:\myProject").
I prefer the null version, because there is no need to run any installer. Moreover, you tin can simply delete the entire Eclipse directory when information technology is no longer needed (without running any un-installer). You lot are complimentary to move or rename the directory. You can install (unzip) multiple copies of Eclipse in the same machine.
How to Install Eclipse on macOS
To use Eclipse for Coffee programming, you lot demand to showtime install JDK. Read "How to install JDK for macOS".
To install Eclipse:
- Goto http://world wide web.eclipse.org/downloads/package/. Choose "Eclipse IDE for Java Developers" and "macOS x86_64" (for Intel processor). You lot volition receive a DMG file (eastward.chiliad., "
eclipse-coffee-2021-12-R-macosx-cocoa-x86_64.dmg"). - Double-click the downloaded Disk Paradigm (DMG) file. Follow the screen instructions to install Eclipse. Eclipse volition be installed under "
/Applications/eclipse". (To confirm!)
How to Install Eclipse on Ubuntu Linux
Eclipse comes with many flavors (See "Eclipse Packages" @ https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/compare.php):
- To use Eclipse for Java programming, cull "Eclipse IDE for Java Developers" (JavaSE) or "Eclipse IDE for Java EE Developers" (JavaEE). You need to first install JDK. Read "How to install JDK on Ubuntu".
- To apply Eclipse for PHP programming, choose "Eclipse IDE for PHP Developers".
- To utilise Eclipse for C/C++ programming, choose "Eclipse IDE for C/C++ Developers".
Nonetheless, you can install whatever parcel, and then add more features when needed.
To install Eclipse (due east.grand, for Coffee Programming):
- Download Eclipse from http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/. Under "Get Eclipse IDE 2020-12" ⇒ Click the link "Download Packages" (instead of pushing the button "Download x86_64"). Choose "Eclipse IDE for Java Developers" for Java SE program development; or "Eclipse IDE for Java EE Developers" for developing webapps ⇒ Linux x86_64. Yous will receive a tarball (e.g., "
eclipse-java-2020-12-R-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz") in the "~/Downloads" binder. - Nosotros shall install Eclipse under
/usr/local.$ cd /usr/local $ sudo tar xzvf ~/Downloads/eclipse-java-2020-12-R-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz $ cd /usr/bin $ sudo ln -south /usr/local/eclipse/eclipse $ ls -ld /usr/bin/eclipse lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 26 Aug 30 11:53 /usr/bin/eclipse -> /usr/local/eclipse/eclipse $ which eclipse /usr/bin/eclipse
To run Eclipse, open the "/usr/local/eclipse" folder and click on the "Eclipse" icon; or get-go a "Terminal", enter "eclipse".
Lock Eclipse on Launcher
Just start Eclipse. Right-click the Eclipse icon ⇒ "Lock to Launcher" or "Add to Favourite".
(For older version - If the above don't work) Create a /usr/share/applications/eclipse.desktop file with the following contents:
[Desktop Entry] Name=Eclipse Type=Awarding Exec=eclipse Last=simulated Icon=/usr/local/eclipse/icon.xpm Comment=Integrated Evolution Environment NoDisplay=false Categories=Evolution;IDE; Name[en]=Eclipse
Start Eclipse, correct-click on the Eclipse icon on launcher ⇒ "Lock to launcher".
Writing your First Java Program in Eclipse
Step 0: Launch Eclipse
- Launch Eclipse past running "
eclipse.exe" from the Eclipse installed directory. - Choose an appropriate directory for your workspace, i.east., where you lot would like to save your files (e.g.,
c:\myProject\eclipsefor Windows) ⇒ Launch. - If the "Welcome" screen shows upwards, close it by clicking the "close" button side by side to the "Welcome" title.
Pace 1: Create a new Java Project
For each Java application, yous need to create a project to proceed all the source files, classes and relevant resource.
To create a new Java project:
- Choose "File" menu ⇒ "New" ⇒ "Java projection" (or "File" ⇒ "New" ⇒ "Project" ⇒ "Java project").
- The "New Coffee Project" dialog pops up.
- In "Projection name", enter "
FirstProject". - Check "Use default location".
- In "JRE", select "Employ an execution environment JRE (JavaSE-17). Make sure that your JDK is 11 and higher up.
- In "Project Layout", check "Utilise project folder as root for sources and class files".
- In "Module", UNCHECK "Create module-info.java" file.
- In "Projection name", enter "
- IF "Create module-info.coffee" dialog appears, Click "Don't Create".
Step 2: Write a Hello-world Java Plan
- In the "Package Explorer" (left pane) ⇒ Correct-click on "
FirstProject" (or use the "File" menu) ⇒ New ⇒ Form. - The "New Java Class" dialog pops up.
- In "Source binder", keep the "FirstProject".
- In "Parcel", leave information technology EMPTY. Delete the content if it is non empty.
- In "Name", enter "
Hello". - Check "
public static void main(Cord[] args)". - Don't change the rest.
- The source file "
Hi.java" opens on the editor panel (the middle pane). Enter the post-obit codes:public class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello, world!"); } }
Step 3: Compile & Execute the Java Program
- There is no need to compile the Coffee source file in Eclipse explicitly. It is because Eclipse performs the so-chosen incremental compilation, i.east., the Java statement is compiled as and when information technology is entered.
- To run the program, right-click anywhere on the source file "
Hello.coffee" (or cull "Run" bill of fare) ⇒ Run Every bit ⇒ Java Awarding. - The output "Hello, world!" appears on the Console panel (the bottom pane).
NOTES:
- You should create a NEW Java project for EACH of your Java awarding.
- Nonetheless, Eclipse allows yous to continue more i programs in a project, which is handy for writing toy programs (such as your tutorial exercises). To run a particular program, open and right-click on the source file ⇒ Run As ⇒ Java Application.
- Clicking the "Run" button (with a "Play" icon) runs the recently-run program (based on the previous configuration). Effort clicking on the "downward-arrow" besides the "Run" button.
Correcting Syntax Errors
Eclipse performs incremented compilation, as and when a source "line" is entered. Information technology marked a source line having syntax error with a RED CROSS. Place your cursor at the Cerise CROSS to view the fault bulletin.
You lot CANNOT RUN the program if there is any syntax fault (marked by a Reddish Cantankerous before the filename). Correct all the syntax errors; and RUN the plan.
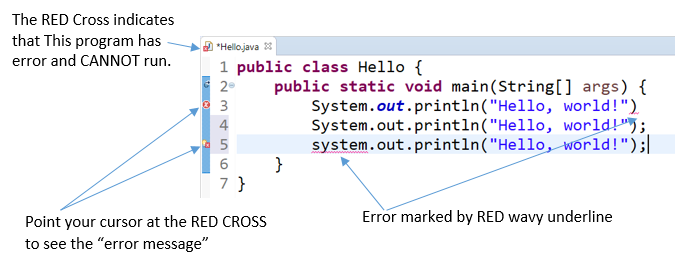
HINTS: In some cases, Eclipse shows a Orange LIGHT-BULB (for HINTS) next to the Fault RED-Cross (Line 5 in the above diagram). You can click on the LIGHT-Seedling to get a list of HINTS to resolve this particular mistake, which may or may not piece of work!
SYNTAX WARNING: marked by a orangish triangular exclaimation sign. Different errors, warnings may or may not cause problems. Try to fix these warnings as well. But y'all can RUN your program with warnings.
Read the Eclipse Documentation
At a minimum, you SHOULD browse through Eclipse's "Workbench User Guide" and "Java Development User Guide" - accessible via the Eclipse'southward "Welcome" folio or "Assistance" menu. This will save you lot many agonizing hours trying to effigy out how to do somethings subsequently.
Debugging Programs in Eclipse
Able to employ a graphics debugger to debug program is crucial in programming. It could relieve y'all countless hours guessing on what went wrong.
Step 0: Write a Java Program
The post-obit program computes and prints the factorial of n (=1*ii*3*...*n ). The programme, all the same, has a logical fault and produce a wrong answer for n =20 ("The Factorial of 20 is -2102132736" - a negative number?!).
1 2 3 four five half-dozen 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | public class Factorial { public static void main(Cord[] args) { int n = xx; int factorial = i; int i = 1; while (i <= n) { factorial = factorial * i; i++; } System.out.println("The Factorial of " + northward + " is " + factorial); } } |
Allow's use the graphic debugger to debug the plan.
Step 1: Prepare an Initial Breakpoint
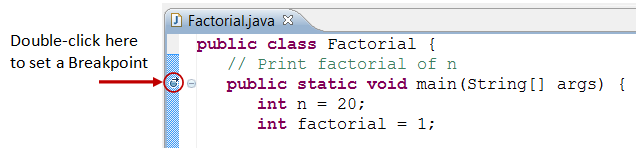
A breakpoint suspends program execution for you to examine the internal states (eastward.1000., value of variables) of the plan. Earlier starting the debugger, you demand to set at least one breakpoint to append the execution inside the program. Set a breakpoint at main() method by double-clicking on the left-margin of the line containing chief(). A blue circle appears in the left-margin indicating a breakpoint is prepare at that line.
Step 2: Start Debugger
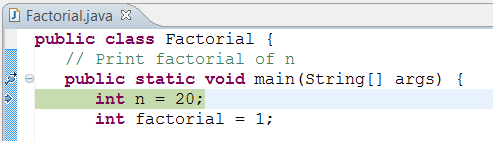
Correct click anywhere on the source code (or from the "Run" menu) ⇒ "Debug As" ⇒ "Java Application" ⇒ choose "Yes" to switch into "Debug" perspective (A perspective is a particular arrangement of panels to suits a certain development task such every bit editing or debugging). The program begins execution merely suspends its operation at the breakpoint, i.eastward., the chief() method.
As illustrated in the following diagram, the highlighted line (also pointed to by a blue arrow) indicates the argument to exist executed in the next footstep.
Footstep 3: Step-Over and Spotter the Variables and Outputs
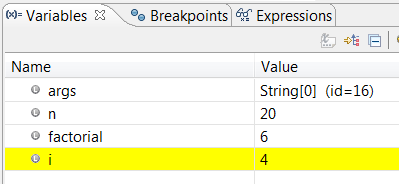
Click the "Step Over" push (or select "Footstep Over" from "Run" card) to single-step thru your program. At each of the step, examine the value of the variables (in the "Variable" console) and the outputs produced past your program (in the "Console" Console), if any. Y'all can too place your cursor at any variable to inspect the content of the variable.
Single-stepping thru the program and watching the values of internal variables and the outputs produced is the ultimate mean in debugging programs - because it is exactly how the computer runs your program!
Step 4: Breakpoint, Run-To-Line, Resume and Finish
As mentioned, a breakpoint suspends program execution and allow you examine the internal states of the program. To set up a breakpoint on a particular argument, double-click the left-margin of that line (or select "Toggle Breakpoint" from "Run" menu).
"Resume" continues the program execution, upward to the side by side breakpoint, or till the end of the programme.
"Single-step" thru a loop with a large count is time-consuming. You could prepare a breakpoint at the statement immediately outside the loop (e.g., Line eleven of the in a higher place plan), and upshot "Resume" to consummate the loop.
Alternatively, y'all can place the cursor on a particular argument, and outcome "Run-To-Line" from the "Run" bill of fare to continue execution up to the line.
"Terminate" ends the debugging session. Always finish your current debugging session using "Stop" or "Resume" till the cease of the program.
Step five: Switching Back to Java perspective
Click the "Java" perspective icon on the upper-correct corner to switch back to the "Java" perspective for further programming (or "Window" menu ⇒ Open Perspective ⇒ Java).
Important: I can'southward stress more that mastering the utilize of debugger is crucial in programming. Explore the features provided by the debuggers.
Other Debugger'due south Features
Step-Into and Step-Return: To debug a method, you need to employ "Step-Into" to step into the offset statement of the method. ("Step-Over" runs the function in a single pace without stepping through the statements inside the function.) You lot could apply "Pace-Return" to return back to the caller, anywhere within the method. Alternatively, y'all could set a breakpoint within a method.
Modify the Value of a Variable: Yous can modify the value of a variable past entering a new value in the "Variable" panel. This is handy for temporarily modifying the beliefs of a plan, without changing the source code.
Tips & Tricks
General Usages (for all Programming Tasks)
These are the features that I find to be well-nigh useful in Eclipse:
- Maximizing Window (Double-Clicking): You can double-click on the "header" of any console to maximize that particular panel, and double-click again to restore it dorsum. This feature is specially useful for writing source code in full panel.
- Shorthand Templates (sysout, for,...): You can blazon "
sysout" followed by a ctrl+space (or alt-/) as a shorthand for typing "System.out.println()".
The default shortcut key (ctrl-infinite or alt-/) depends on the organisation. Bank check your system'south shortcut cardinal setting in "Edit" ⇒ "Content Assist" ⇒ "Default". Take annotation that many of y'all use ctrl+space to switch betwixt input languages. You need to reconfigure either your language switching hot-primal or Eclipse.
Similarly, you tin can type "for" followed past ctrl-space (or alt-/) to go a for-loop.
You lot can create your own shorthand in "Window" bill of fare ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ "Java" ⇒ "Editor" ⇒ "Templates". (Alternatively, in "Window" ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ type "template" as filter text and choose "Coffee" ⇒ "Editor" ⇒ "Templates".)
You can modify your primal settings in "Window" menu ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ "General" ⇒ "Key" ⇒ choose "Command", "Content Assistance". (Alternatively, in "Window" ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ type "key" every bit filter text and choose "General" ⇒ "Key".) - Intelli-Sense (ctrl-infinite): You tin can use ctrl-space to activate the "intelli-sense" (or content assist). That is, Eclipse volition offer y'all the choices, while you are typing.
- Source Formatting (ctrl-shift-f): Right-click on the source. Choose "Source" ⇒ "Format" to let Eclipse to layout your source codes with the proper indentation.
- Source Toggle Comment (ctrl-/): To annotate/uncomment a block of codes, choose "Source" ⇒ "Toggle Comment".
- Hints for Correcting Syntax Mistake: If there is a syntax error on a statement, a red mark volition evidence upwardly on the left-margin on that statement. You could click on the "lite bulb" to display the error message, and also select from the available hints for correcting that syntax error.
- Refactor (or Rename) (alt-shift-r): You tin rename a variable, method, grade, packet or fifty-fifty the project easily in Eclipse. Select and correct-click on the entity to be renamed ⇒ "Refactor" ⇒ "Rename". Eclipse can rename all the occurrences of the entity.
- Line Numbers: To show the line numbers, cull "Window" menu ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ "Full general" ⇒ "Editors" ⇒ "Text Editors" ⇒ Check the "Prove Line Numbers" Box. Yous can also configure many editor options, such as the number of spaces for tab. Alternatively, you can right-click on the left-margin, and bank check "Show Line Numbers".
- Error Message Hyperlink: Click on an error message will hyperlink to the corresponding source statement.
- Changing Font Type and Size: From "Window" menu ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ "General" ⇒ "Appearance" ⇒ "Colors and Fonts" ⇒ aggrandize "Java" ⇒ "Java Editor Text Font" ⇒ "Edit". (Alternatively, in "Window" ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ type "font" as filter text and choose the advisable entry.)
- Unicode Back up: To enable Unicode back up, select "Window" menu ⇒ Preferences ⇒ General ⇒ Workspace ⇒ Text file encoding ⇒ UTF-8. This sets the default grapheme set used for file encoding, like to VM's command-line option
-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8. Commonly used charsets for Unicode are UTF-viii, UTF-xvi (with BOM), UTF-16BE, UTF-16LE. Other charsets are United states of america-ASCII, ISO-8859-1. - Mouse Hover-over: In debug mode, you could configure to prove the variable's value when the mouse hovers over the variable. Select "Window" carte ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ "Coffee" ⇒ "Editor" ⇒ "Hover".
- Comparing Two Files: In "Packet Explorer", select two files (hold the control key) ⇒Correct-click ⇒ Compare with.
- Setting Keyboard Shortcut Keys: You can gear up/change the keyboard shortcut keys at "Window" ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ "General" ⇒ "Central".
I similar to fix the frequently-used commands to Ctrl-1 to Ctrl-ten, for examples, "Run Java Application" to "Ctrl-1", etc. - Useful Eclipse Shortcut Keys:
- F3: Goto the declaration of the highlighted variable/method.
- Ctrl-Shift-Thou: Search for ALL references of the highlighted variable/method in workspace.
- Ctrl-1000: Search for the Declaration of a variable/method in workspace.
Don't utilise Find (Ctrl-F), but use the above context-sensitive search. - Ctrl-Shift-F: Format the source code.
- Ctrl-Shift-O: Organize imports.
- Alt-Shift-R: Rename. (Don't use Notice/Supervene upon.)
- Ctrl-Infinite: auto-complete.
- Package Explorer vs. Navigator: We commonly utilise "Package Explorer" in programming, but information technology will not show y'all all the folders and files under the project. On the other hand, "Navigator" is a file manager that shows the exact file structure of the project (similar to Windows Explorer). You tin can enable the Navigator by "Window" ⇒ Show view ⇒ Navigator.
- Spell Bank check: To enable spell check, select Window ⇒ Preferences ⇒ type "spell" in the filter ⇒ Full general ⇒ Editors ⇒ Text Editors ⇒ Spelling ⇒ Cheque "Enable spell checking". Too provide a "User defined dictionary" (with an initially empty text file).
To correct mis-spell words, correct-click and press ctrl-1 (or Edit carte du jour ⇒ Quick Fix). - Eclipse's Log File: Goto Assist ⇒ about Eclipse ⇒ Installation details ⇒ Configuration ⇒ View Error Log.
- Viewing two files in carve up screen: Simply click and concur on the championship of one file and drag it to the lower side of the screen. [To view the aforementioned file on divide screen, create a new editor window by selecting Window ⇒ New Editor; and drag i window to the lower side of the screen.]
- Cake Select (Column Select): Push Alt-Shift-A to toggle between block-select mode and normal mode.
- Snippets:
- To view the snippet window: choose "Window" ⇒ Show View ⇒ Snippets.
- To create a new snippet category: Right-click ⇒ Customize ⇒ New.
- To create a new snippet item: Copy the desired text ⇒ Select the snippet category ⇒ paste as snippet.
- To insert a snippet: place the cursor on the desired location at the editor panel ⇒ click the snippet detail.
- Word Wrap (Line Wrap): Word-wrap (or line-wrap) is essential for editing long HTML documents without the horizontal scroll bar. Even so, the Eclipse's HTML Editor and Text Editor do not back up word-wrap.
You could install a plug-in chosen "Word Wrap" from http://ahtik.com/eclipse-update/.
Cull "Help" ⇒ Install New Software ⇒ in "Work with" Enter "http://ahtik.com/eclipse-update/".
To activate give-and-take wrap, correct-click on the editor panel ⇒ select "Give-and-take Wrap". - Creating "link folder" in projection: Y'all practise not have to place all the folders under the project base directory, instead, you lot tin use so-called "link folders" to link to folder outside the project base directory.
To create a link folder in a projection, right-click on the project ⇒ File ⇒ New ⇒ Binder ⇒ Advanced ⇒ Check Link to alternate Location (Linked Folder). - Running Eclipse in "clean" mode: You can run eclipse in then-called "
make clean" manner, which wipes all the cached data and re-initialize the enshroud, by running eclipse from command-line with "-make clean" statement (i.e., "eclipse -clean"). It is useful if something is not working proper, especially if you lot install a new copy of Eclipse. - Bear witness the Correct Margin: Window ⇒ Preferences ⇒ General ⇒ Editors ⇒ Text Editors ⇒ Show Impress Margin and prepare the cavalcade number.
- Allow me know if you have more tips to exist included here.
Update Eclipse and Install new Software
- Install New Software: Select "Help" card ⇒ Install New Software ⇒ In "Piece of work With", pull down the select menu and choose a software site.
- Update: Select "Help" menu ⇒ Check for Updates ⇒.
For Java Application Evolution But
- Small Toy Java Programs: You lot can go on many small-scale programs (with
main()) in one Java project instead of create a new projection for each toy program. To run the desired plan, right-click on the source file ⇒ "Run every bit" ⇒ "Java Application". - Scanner/printf() and JDK one.5: If yous run into syntax fault in using
printf()orScanner(which are available from JDK ane.v), you need to check your compiler settings. Select "Window" menu ⇒ Preferences ⇒ open the "Coffee" node ⇒ select "Compiler" ⇒ in "Compiler compliance level" ⇒ select the latest release, which should be "1.5" or above. - Command-Line Arguments: To provide command-line arguments to your Java program in Eclipse, right-click on the source file ⇒ "Run Configurations" ⇒ Nether the "Chief" panel, check that "Project" name and "Main Class" are advisable ⇒ Select the "Argument" tab ⇒ type your command-line arguments within the "Program Arguments" box ⇒ "Run".
- Resolving Import (Ctrl-Shift-o): To ask Eclipse to insert the
importstatements for classes. Useful when you lot re-create a big chunk of codes without the corresponding import statements. - Including Another Project: To include another projection in the same piece of work space, correct-click on the projection ⇒ Build Path ⇒ Configure Build Path... ⇒ Select "Projects" tab ⇒ "Add..." to select project in the existing work space ⇒ OK.
- Exporting a Project to a JAR file: Correct-click on the project ⇒ Export... ⇒ Java, JAR File ⇒ Side by side ⇒ Select the files to exist exported ⇒ Next ⇒ Next ⇒ In "JAR Manifest Specification" dialog, enter the chief course (if you wish to run the JAR file directly) ⇒ Finish.
- Unit Testing: If you go along your test in another project, yous need to include the projection under test in your Build Path (encounter to a higher place).
To create a exam case: Right-click on the project ⇒ New ⇒ JUnit Examination Example ⇒ the "New JUnit Test Instance" dialog appears. Select "New JUnit 4 Examination". In "Name", enter your class name. In "Class under test", browse and select the class to be tested.
To run the test: Right-click ⇒ "Run As" ⇒ "JUnit Test". The results are displayed in a special "JUnit panel". - Adding External JAR files & Native Libraries (".dll", ".lib", ".a", ".then"): Many external Java packages (such every bit JOGL, Java3D, JAMA, etc) are bachelor to extend the functions of JDK. These packages typically provide a "
lib" directory containing JAR files (".jar") (Java Annal - a single-file package of Coffee classes) and native libraries (".dll", ".lib" for windows, ".a", ".so" for Linux and macOS).
To include these external packages into an Eclipse's projection, right-click on the project ⇒ Build Path ⇒ Add together External Athenaeum ⇒ Navigate to select the JAR files (".jar") to exist included.
In "Bundle Explorer", right-click on the JAR file added ⇒ Properties:- To include native libraries ("
.dll", ".lib", ".a", ".so"), select "Native Library" ⇒ "Location Path" ⇒ "External Folder". - To include the javadoc, select "JavaDoc Location" ⇒ "JavaDoc URL" ⇒ You lot can specify a local file or a remote link.
- To include source file (for debugging), select "Coffee Source Attachment".
Notes: The JAR files must exist included in theCLASSPATH. The native library directories must be included in JRE's holding "java.library.path", which normally but not necessarily includes all the paths from thePATHenvironment variable. Read "External JAR files and Native Libraries". - To include native libraries ("
- Creating a User Library: You lot can also create a Eclipse's user library to include a set of JAR files and native libraries, that can then be added into subsequent Eclipse projects.
For case, I created a user library for "JOGL" as follows:
- From "Window" menu ⇒ Preferences ⇒ Java ⇒ Build Path ⇒ User Libraries ⇒ New ⇒ In "User library name", enter "
jogl". The "User Library" dialog appears. - In "User Library" dialog ⇒ Select "
jogl" ⇒ Add JAR... ⇒ Navigate to<JOGL_HOME>/lib, and select "gluegen-rt.jar" and "jogl.jar". - Aggrandize the "
jogl.jar" node ⇒ Select "Native library location: (none)" ⇒ Edit... ⇒ External Folder... ⇒ select<JOGL_HOME>/lib. - Expand the "
jogl.jar" node ⇒ Select "Javadoc location: (none)"⇒ Edit... ⇒ Javadoc in archive ⇒ In "Archive Path", "Scan" and select the downloaded JOGL API documentation zip-file ⇒ In "Path inside archive", "Browse" and expand the aught-file to select the top-level path (if any) ⇒ Validate. Alternatively, you tin provide the path to the un-zipped javadocs. This is needed for Eclipse to display javadoc information about classes, fields, and methods. - You may provide the source files by editing "Source zipper: (none)". Source is needed only if yous are interested to debug into the JOGL source codes.
jogl". - From "Window" menu ⇒ Preferences ⇒ Java ⇒ Build Path ⇒ User Libraries ⇒ New ⇒ In "User library name", enter "
- Running an External Programme: Suppose that you want to run a Perl script on the selected file, you can configure an external tool as follows:
- From "Run" card ⇒ External Tools ⇒ External Tools Configuration... ⇒ The "External Tools Configuration" dialog appears.
- In "Proper name", enter your tool proper noun.
- Choose the "Main" tab ⇒ In "Location", "Browse File System..." to choose the perl interpreter "perl" ⇒ In "Arguments", enter "
path/scriptname.pl ${resource_loc}", where${resource_loc}is an Eclipse variable that denotes the currently selected resources with accented path. - Choose the "Common" tab ⇒ In "Standard Input and Output", uncheck "Allocate Console", check "File" and provide an output file (east.g.,
d:\temp\${resource_name}.txt). - (If y'all use the CYGWIN perl interpreter, demand to set up environs variable CYGWIN=nodosfilewarning to disable alarm message.)
- Viewing Hex Code of Primitive Variables in Debug mode: In debug perspective, "Variable" panel ⇒ Select the "menu" (inverted triangle) ⇒ Coffee ⇒ Java Preferences... ⇒ Primitive Display Options ⇒ Check "Display hexadecimal values (byte, brusk, char, int, long)".
- Adding a New Version of JDK/JRE: First, you can check the installed JDK/JRE via "Window" menu ⇒ "Preferences" ⇒ Expand "Java" node ⇒ "Installed JREs". Check the "Location" current JRE installed to brand certain that it is the intended one. You can use the "Add" button to add together a new version of JRE. For program development, I recommend that you add together the JDK (instead of JRE). [The "Location" decides the extension directory used for including boosted JAR files, e.g.,
$JAVA_HOME\jre\lib\ext.]
For Spider web Developers
- HTML Editor: Use the "Spider web Page Editor" (bachelor in Eclipse Java EE), which provides the pattern view (WYSISYG).
To use the "Spider web Folio Editor", correct-click on the HTML file, open as "Web Page Editor".
To brand the "Spider web Page Editor" as default for HTML file, goto Window ⇒ Preferenes ⇒ General ⇒ Editor ⇒ File Associations ⇒ .htm and .html ⇒ Select "Web folio editor" ⇒ default.
File I/O in Eclipse
Suppose that your want to write a Java program, which inputs from a text file chosen "xxxx.in" and outputs to a text file chosen "xxxx.out". This is a little tricky under Eclipse due to:
- When you create a text file in Windows' Notepad and saved it equally "
xxxx.in", Notepad volition append the ".txt" to your file and it becomes "xxxx.in.txt". Worse nonetheless, the Windows' Explorer, by default, will not bear witness the ".txt" extension. (The outset thing I ever do to an alien computer is to change this setting. From "Tools" menu ⇒ Folder Options... ⇒ View ⇒ Uncheck "Hide extensions for known file types".) Yous need to put a pair of double quotes aroundxxxx.into override the default ".txt" extension. This is one skillful reason non to utilise Notepad for programming at all. You lot should use Eclipse to create the text file instead. - Which directory to keep the input file "
xxxx.in" in Eclipse?- If you did not separate the sources and grade files into two divide directories, then the respond is straight forward, considering there is only one directory to place your input file.
- If yous choose to keep your sources and class files in two separate directories, eclipse will create two sub-directories "src" and "bin" under the base of operations directory. BUT you need to put your input file "
xxxx.in" in the base of operations directory of your projection, instead of the "src" or "bin"..
For writing simple programs:
- Put the sources, course files, and the input/output files in the same directory. (When you create a new project, select "Apply projection folder as root for sources and course files" in "Project Layout".) (But put your sources and class files in separate directories for big projection.)
- You can create you input file from eclipse direct via "File" card ⇒ "New" ⇒ "File".
- Recollect to add together a newline to the end of your input file.
- You may need to correct-click the project and select "Refresh" to meet the output file "
xxxx.out" created in the package explorer. - To open the "
xxxx.in" and "xxxx.out": right-click ⇒ Open With ⇒ Text Editor.
This is a sample JDK ane.5 programme for file input/output:
import coffee.util.Scanner; import java.util.Formatter; import java.io.File; import coffee.io.IOException; public class FileIOTest { public static void main (String [] args) throws IOException { Scanner in = new Scanner(new File("FileIOTest.in")); Formatter out = new Formatter(new File("FileIOTest.out")); int a = in.nextInt(); int b = in.nextInt(); out.format("%d\due north",a+b); out.close(); } } Create the input text file called "FileIOTest.in" with the following contents and terminated with a newline:
55 66
Writing Swing Applications using Eclipse GUI Builder
Eclipse provides a visual GUI builder called "WindowBuilder" (@ https://www.eclipse.org/windowbuilder), which supports AWT/Swing, SWT (Eclipse's Standard Widget Toolkit - an alternative to JDK's AWT/Swing), XWT, GWT, eRCT.
Stride 0: Install WindowBuilder
To install "WindowBuilder", goto "Help" ⇒ Install New Software ⇒ In "Piece of work with", enter "https://download.eclipse.org/windowbuilder/latest/" (Yous tin find the proper link from "http://world wide web.eclipse.org/windowbuilder/download.php") ⇒ Cheque "WindowBuilder" ⇒ Next ⇒ Next ⇒ Accept the licence ⇒ Finish.
Step 1: Create a New "Java Application" Project
- Choose "File" menu ⇒ "New" ⇒ "Java project".
- The "New Java Projection" dialog pops up.
- In the "Projection name" field, enter "
FirstSwingProject". - Bank check "Utilize default location".
- In the "JRE" box, select "Use default JRE (currently 'JDK1.x')".
- Click "Finish".
- In the "Projection name" field, enter "
Step 2: Create a Swing JFrame Subclass
- Choose "File" menu ⇒ "New" ⇒ "Others" ⇒ "WindowBuilder" ⇒ "Swing Designer" ⇒ "JFrame" ⇒ "Adjacent".
- In the "Create JFrame" dialog ⇒ Enter "SwingMain" in the "Name" field ⇒ "Finish".
- Select the "Blueprint" pane.
- In "Layouts", select "FlowLayout" and click on the "design form".
- From "Components", select "
JLabel" and click on the pattern course. Change the label text to "Counter: ". Select a "JTextField" and place it on the design form. Change the text to "0". Select a "JButton" and identify it on the pattern form. Change the text characterization to "Count". - To adhere a event-handler to the button, double-click the
JButtonto switch into the "Source" pane, with the consequence-handler skeleton created. Complete theactionPerformed()equally follows:public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent due east) { count++; textField.setText(count + ""); }Add an instance variable chosencountevery bit follow:public grade SwingMain extends JFrame { private int count = 0; ...... - You lot can now set run the program. Right-click on the project ⇒ Run As ⇒ Java Application.
Eclipse Generated Codes
Study the codes generated by Eclipse GUI Builder, as follows, which is just a typical Swing awarding.
ane ii three 4 5 6 vii 8 9 ten 11 12 13 xiv 15 16 17 18 19 xx 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 xxx 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 | import java.awt.*; import coffee.awt.consequence.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.edge.EmptyBorder; public form SwingMain extends JFrame { private JPanel contentPane; private JTextField textField; private int count = 0; public static void chief(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { endeavor { SwingMain frame = new SwingMain(); frame.setVisible(true); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } public SwingMain() { setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); setBounds(100, 100, 450, 300); contentPane = new JPanel(); contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(v, v, 5, 5)); setContentPane(contentPane); contentPane.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.Middle, 5, 5)); JLabel lblNewLabel = new JLabel("Counter: "); contentPane.add(lblNewLabel); textField = new JTextField(); textField.setText("0"); contentPane.add together(textField); textField.setColumns(10); JButton btnCount = new JButton("Count"); btnCount.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { count++; textField.setText(count + ""); } }); contentPane.add(btnCount); } } |
Eclipse for C/C++ Programming
Here.
Eclipse PDT (PHP Development Tool)
Here.
Eclipse-JavaEE and Database Development
Reference: "Information Tools Platform User Documentation" @ Eclipse Welcome page.
You need to install:
- "Eclipse for Java EE" (aka "Eclipse IDE for Enterprise Java Developers").
- "MySQL Community Server" and "MySQL Connector/J Driver". Read "How to install and get started with MySQL".
To use Eclipse for MySQL development:
- Switch to "Database Evolution" perspective:
From "Window" menu ⇒ Open Perspective ⇒ Other ⇒ Database Development. - Create a Database Connection: Starting time your MySQL database server ⇒ Right-click "Database Connectedness" ⇒ New. Take note that each database connection connect to ONE item database in the database server with a URL in the form of jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/database-name.
- In "Connectedness Contour", choose "MySQL" ⇒ Next.
- In "Drivers", click the icon for "New Driver Definition" (if the commuter has not been divers).
- In "Specify a Driver Template and Definition Proper name":
- Cull the "Name/Type" tab ⇒ Choose i of the database driver as our template (east.g. MySQL 5.1) for further customization ⇒ Set your "Driver name", e.k., "mysql-connector-java-8.0.23".
- Switch to "JAR List" tab ⇒ Articulate All ⇒ Click "Add JAR/Nada" and select the commuter JAR file, e.g., mysql-connector-java-viii.0.23.jar.
- Switch to "Properties" tab ⇒ Check the parameters.
- OK.
- Enter the "Database" name, URL (with the same database proper name), and the "Countersign" ⇒ Click "Test Connection"
- Finish.
- In "Datasource Explorer", you can "connect" and "disconnect" the connection.
- To view and edit tabular array visually, expand database "Schemas" to await for the table. Right-correct on the table ⇒ Information ⇒ Edit. Yous tin can alter the cells and "salvage" the changes.
- To create a new SQL script, choose File ⇒ New ⇒ SQL File ⇒ You may utilize an existing project or create a new projection (General|Projection or Web|Dynamic Spider web Projection) ⇒ Enter filename, and set the connexion profile proper noun ⇒ Finish. Enter a SQL statement (e.g., SELECT * FROM tablename) ⇒ Right-click on the text ⇒ "Execute Current Text" or "Execute All".
- To utilise an existing SQL file, drib the file into a projection and open the SQL file. In Connection profile, set the type and connection name. Right-click on a statement ⇒ "Execute ...".
Developing and Deploying Webapps in Eclipse-JavaEE
Setting Up Eclipse-JavaEE for Web Evolution
- Install "Eclipse for Coffee EE" (aka "Eclipse IDE for Enterprise Java Developers").
- Install Tomcat (or Glassfish) server.
- Configuring Web Server: Launch Eclipse ⇒ Window ⇒ Preferences ⇒ Expand the "Server" node ⇒ "Runtime Environments" ⇒ "Add..." ⇒ Aggrandize "Apache" and select "Apache Tomcat vX.X" ⇒ Enter your "Tomcat Installation Directory" ⇒ "Finish".
Writing a Hi-earth Servlet
- Switch to "Java EE" perspective (which is the default perspective for Eclispe-JavaEE):
From "Window" menu ⇒ Open up Perspective ⇒ Other ⇒ Coffee EE. - Create a new Web Awarding Projection: from "File" ⇒ New ⇒ Dynamic Web Project (under "Web" category) ⇒ In "Projection Proper name", enter "
HelloServletProject" ⇒ "Finish". - Create a new Servlet: Right-click on the project "
HelloServletProject" ⇒ New ⇒ Servlet ⇒ In "Java Package", enter "mypkg"; in "Class Proper noun", enter "HelloServlet" ⇒ Next ⇒ In "URL Mappings", select "/HelloServlet" ⇒ "Edit" to "/sayhello" ⇒ Adjacent ⇒ In "Which method stubs would you similar to create", check "Inherited abstract method", "doGet" and "doPost" (default) ⇒ End.
In "HelloServlet.java", enter the following codes:package mypkg; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.notation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; @WebServlet("/sayhello") public form HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { private static last long serialVersionUID = 1L; public HelloServlet() { super(); } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("<!DOCTYPE html>"); out.println("<html>"); out.println("<head><championship>Hullo Servlet</title></head>"); out.println("<body>"); out.println("<h1>Hi World, from Servlet!</h1>"); out.println("<p>Method: " + request.getMethod() + "</p>"); out.println("<p>Request URI: " + asking.getRequestURI() + "</p>"); out.println("<p>Protocol: " + asking.getProtocol() + "</p>"); out.println("<p>PathInfo: " + request.getPathInfo() + "</p>"); out.println("<p>Remote Address: " + request.getRemoteAddr() + "</p>"); out.println("<p>Generate a Random Number per asking: <strong>" + Math.random() + "</stiff></p>"); out.println("</trunk>"); out.println("</html>"); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(asking, response); } }(For Servlet ii.4/2.5 with Tomcat vi) The notation
@WebServletis new in Servlet 3.0 and is not supported in Servlet 2.4/two.five. Hence, yous need to manually configure the URL for the servlet in the Spider web Application Deployment Descriptor "web.xml" under directory "WEB-INF", as follows:<?xml version="i.0" encoding="ISO-8859-i"?> <spider web-app xmlns="http://coffee.lord's day.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" version="3.0" metadata-complete="true"> <servlet> <servlet-name>HelloServletExample</servlet-proper name> <servlet-class>mypkg.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-proper name>HelloServletExample</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/sayhello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </spider web-app>
- To execute the Servlet, right-click on the "
HelloServletProject" ⇒ "Run As" ⇒ "Run on Server" ⇒ Modify the URL to "http://localhost:8080/HelloServletProject/sayhello".
Writing a Hello-earth JSP (Java Server Pages)
- Create a new Spider web Awarding: File ⇒ New ⇒ Dynamic Spider web Project (under "Spider web" category) ⇒ In "Projection Name", enter "
HelloJSPProject" ⇒ End. - Create a new JSP File: Right-click on the project "
HelloJSPProject" ⇒ New ⇒ JSP File ⇒ The parent folder shall be "HelloJSPProject/WebContent" ⇒ In "File Proper noun", enter "how-do-you-do.jsp" ⇒ "Terminate". - Enter the post-obit HTML/JSP codes:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-ane"> <championship>How-do-you-do JSP</title> </head> <trunk> <h1>Howdy Earth, from JSP</h1> <p>Method: <%= request.getMethod() %></p> <p>Request URI: <%= request.getRequestURI() %></p> <p>Protocol: <%= asking.getProtocol() %></p> <p>PathInfo: <%= request.getPathInfo() %></p> <p>Remote Address: <%= request.getRemoteAddr() %></p> <% double num = Math.random(); if (num > 0.75) { %> <h2>Y'all'll have a lucky day!</h2><p>(<%= num %>)</p> <% } else { %> <h2>Well, life goes on ... </h2><p>(<%= num %>)</p> <% } %> <h3><a href="<%= request.getRequestURI() %>">Endeavour Once again</a></h3> </body> </html>
- To execute the JSP, correct-click on "
how-do-you-do.jsp" ⇒ Run As ⇒ Run on Server.
Exporting a Webapp equally a WAR file
Right-click on the project to be exported ⇒ Consign ⇒ WAR File ⇒ In "Destination", specify the destination directory and filename (the filename shall exist the web application name) ⇒ Finish.
- To deploy the state of war file in Tomcat, simply drop the war file into Tomcat's "
webapps" folder. The war file volition exist automatically extracted and deployed. The web awarding name is the state of war-filename. - You could utilise WinZip (or WinRAR) to view the content of the state of war file, every bit war-file is in ZIP format.
Deploying a webapp exterior the Tomcat'southward webapps directory
To deploy a webapp (called hello) outside the %TOMCAT_HOME%\webapps directory, create a hi.xml file every bit follows and place information technology under the %TOMCAT_HOME%\conf\Catalina\localhost:
<Context displayName="hi" docBase="C:\path\to\webapp" path="/hello" reloadable="true" />
Writing a Howdy-earth JSF (JavaServer Faces)
[TODO]
Debugging Webapps
Y'all can debug a webapp just like standalone application. For case, yous can set breakpoints, unmarried-step through the programs, etc.
REFERENCES & Resources
- Eclipse mother site @ https://www.eclipse.org.
- Eclipse documentation and user guides, attainable via Eclipse's Aid and carte.
Latest version tested: Eclipse Java and Eclipse JavaEE 2021-12
Final modified: January 2022
How To Download Eclipse For Windows 10,
Source: https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/eclipsejava_howto.html
Posted by: ottopairofterl.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Download Eclipse For Windows 10"
Post a Comment